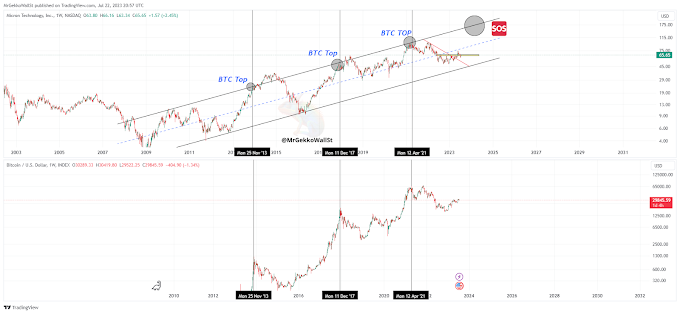
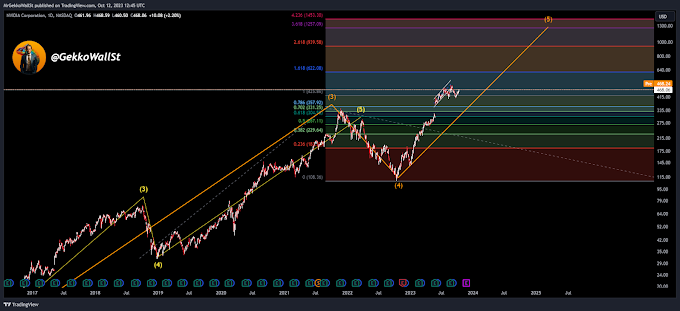
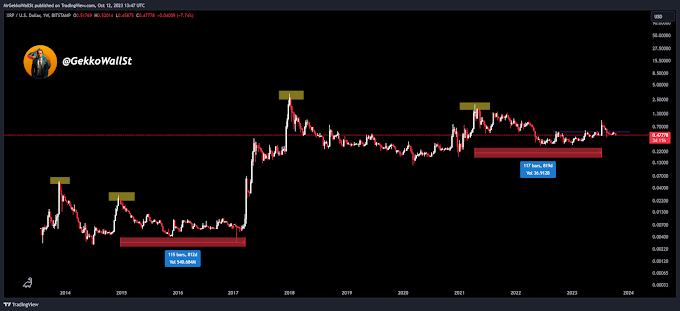
Staking is often associated with blockchains that use a Proof of Stake (PoS) consensus algorithm or its variants. These algorithms eliminate the need for miners solving complex problems to validate transactions and create new blocks, as seen in the Proof of Work (PoW) algorithm used by Bitcoin.
In staking, instead of mining blocks, participants lock a certain amount of coins as a guarantee of their honest participation in the network. This helps ensure the security and integrity of the blockchain. In return, participants can receive rewards in the form of newly created coins (similar to PoW mining) or transaction fees.
Staking rewards can vary based on factors like the specific protocol, the amount of coins locked, the lockup duration, and other parameters set by the cryptocurrency's protocol. Additionally, staking may also involve risks, such as the possibility of losing part or all of the locked coins if network rules aren't followed correctly.
In summary, staking is a way to actively participate in a blockchain network, contributing to its security and validation, while potentially benefiting from rewards in the form of new coins or transaction fees.