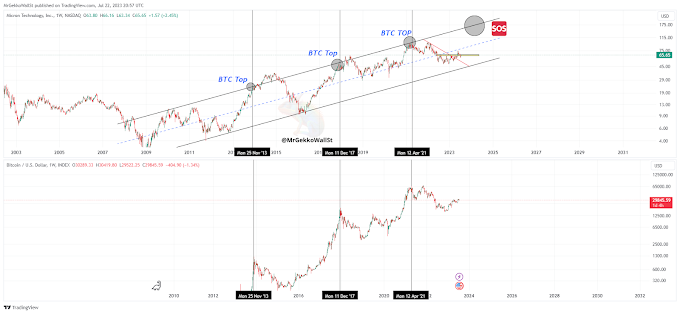
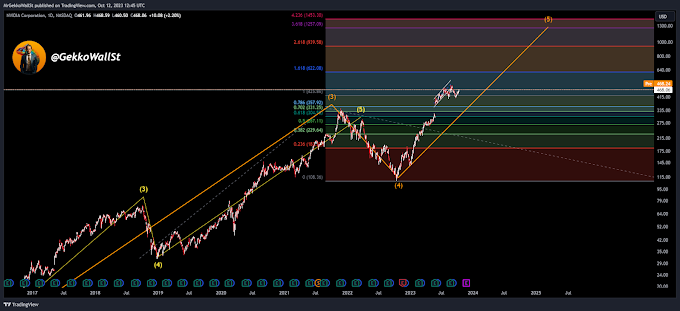
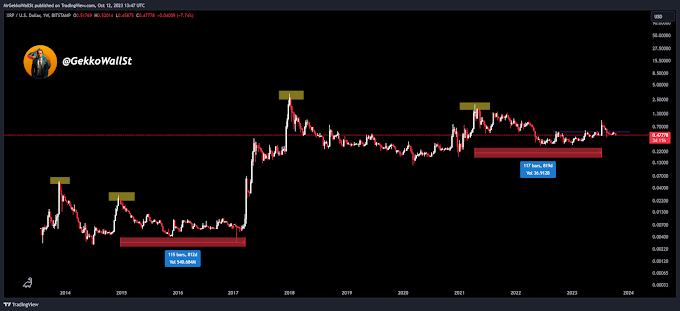
An NFT, or Non-Fungible Token, is a digital representation of unique and indivisible ownership of an asset using blockchain technology. While traditional cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin or Ethereum are fungible and can be exchanged for one another in equal parts, NFTs are unique and not directly interchangeable in terms of value.
NFTs gained popularity primarily in the context of digital art, digital collectibles, music, and other forms of digital media. Each NFT contains unique and verifiable information that establishes the authenticity, ownership, and specific details of the digital asset it's associated with. This allows creators and holders of NFTs to prove ownership of an original copy of a specific digital item.
NFTs are created, bought, and sold on blockchain-based platforms such as Ethereum and Binance Smart Chain. The process usually involves creating a smart contract that defines the unique characteristics of the NFT, such as title, description, associated image or media, as well as information about the creator and ownership rights.
It's important to note that owning an NFT doesn't automatically grant copyright or intellectual property rights over the content it represents. In many cases, the original creators still hold the copyright, while NFT holders own ownership of the specific copy or digital object.
The popularity of NFTs has generated a lot of interest and discussion around their value, environmental impact, regulations, and potential applications beyond art and collectibles, such as in sectors like gaming, music, and virtual property.